What is Dental Trauma

Injury

Dental trauma refers to any injuries to the mouth or mouth area, including the lips, gums, jawbones, tongue, and teeth. Dental injuries are typically very painful and can result in ongoing complications. They should receive prompt first aid treatment.
Ignoring a dental injury can cause serious long-term effects on the mouth and increase the risk of permanent damage. It is essential to get checked out even if it is believed not to be a cause for concern.What is Dental Trauma?
Dental trauma refers to any injuries relating to the mouth, such as teeth, gums, alveolar bone, or the mouth's soft tissue, including lips and tongue. These injuries frequently occur in children and young adults, making up 5% of all dental injuries. School children make up for 25% of dental injuries, and 33% of adults have needed dentistry assistance before the age of 19 because of trauma. Common causes of dental trauma include falls, automobile accidents, interpersonal violence, or sports-related injuries. Patients need to be taken straight to the emergency department if they are suffering severe trauma to the head, neck, or face, such as:- Disorientation
- Dizziness
- Bleeding from ears, nose, or mouth
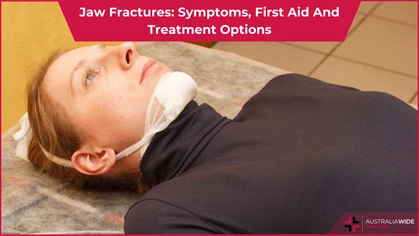
- Fractured jaw
- Concussion
- Memory loss
Common Dental Injuries
Below are some examples of common dental injuries:- Chipped tooth: A chipped tooth occurs when a piece of the tooth enamel, the thin outer covering of the tooth, breaks off. If you chip your tooth, you should book an appointment with your dentist immediately. Though you may not experience significant pain when you chip your tooth, in can lead to infection and additional damage, especially when dentin is exposed. Dentin sits beneath the enamel and cementum, and it is intended to protect the nerves and blood vessels that keep our teeth alive.
- Luxated tooth: Tooth luxation occurs when trauma partly dislodges a tooth from its alveolus, its normal socket in the jaw. A casualty is likely to experience significant pain if one of their teeth becomes luxated, as it disrupts the tissues, ligaments, and bone that hold the tooth in place. It also disrupts the tooth's nerves and blood supply. If you experience tooth luxation, you should consult your dentist immediately, as it can result in necrosis and other complications if left untreated.
- Avulsed tooth: Tooth avulsion occurs when trauma completely dislodges a tooth from its alveolus. In the event of a tooth avulsion, casualties are recommended to reinsert the tooth immediately, and to visit a dentist to stabilise it. If you cannot see a dentist or other healthcare provider immediately, keep the tooth in milk or saline to keep it moist, and to supply it with crucial substances like sugars, proteins, and antibacterial agents.
First Aid for Dental Emergencies
Accidents involving dental injuries can happen to anybody but taking proper measures and knowing what to do is crucial. When you encounter a dental emergency, follow DRSABCD:- D – Danger: Ensure the area is safe and there is no danger surrounding the patient and bystanders.
- R – Response: Is the person conscious? Do they respond when trying to talk to them, touch their hand or squeeze their shoulder? If they are unresponsive, send for help. If they are speaking or moving, monitor them and leave them in the position they were initially found.
- S – Send for help: Get someone to call Triple Zero (000) while you stay with the casualty. If possible, answer as many questions that the operator is asking.
- A – Airway: If the person is unresponsive and not conscious, check their airways and see if any obstructions are in the way. Tilt their head back and pull their chin down to examine if there are any obstructions in the back of the throat. If something is trapping their airflow, position them in the recovery position by placing them on their side, with their neck, spine and head aligned, and perform a finger sweep.
- B – Breathing: Check to see if the patient is breathing. Look to see if their chest rises and falls, listen for any sounds coming out of their mouth and try to feel any air blowing against the cheek. If the breathing is irregular, immediately move on to step C.
- C – CPR: Place the casualty flat on their back and then place a hand on the centre of their chest and the other hand on top of it. Give 30 chest compressions and 2 rescue breaths until the paramedics arrive or the patient starts breathing again.
- D – Defibrillation: If the casualty is still unconscious and not breathing, a defibrillator or AED (automated external defibrillator) is the next step. These can be found in many public places such as clubs and organisations.
Recovering from Dental Trauma
Dental injuries can take up to 6 weeks to heal if there is no damage to the internal nerve of the tooth. It will mostly be inflammation and swelling in the tissue that supports the tooth, such as the gums and bone. However, if there is damage to the internal tooth structure, the dentist may need to do some work on it, such as removing dead and necrotic tissue to prevent infection within the tooth's nerve chamber. If the tooth is not treated, it can cause bleeding from the tissue that can leak into the tooth and cause discolouration. To get it back to its original colour, the dentist may recommend the patient get internal bleaching.References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/dental-trauma
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/dental-injury
- https://www.medicinenet.com/dental_injuries/article.htm
- https://www.ada.org.au/getattachment/Your-Dental-Health/Resources-for-Professionals/Resources-for-Teens-12-17/dental-first-aid-how-to-handle-a-dental-emergency/Dental-first-aid,-how-to-handle-a-dental-emergency.pdf.aspx
- https://www.iadt-dentaltrauma.org/1-9%20%20iadt%20guidelines%20combined%20-%20lr%20-%2011-5-2013.pdf
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/what-is-dental-trauma
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library