Top 5 Leading Causes of Death in Australia

Disease

Though the Australian Bureau of Statistic’s health statistics have been shaken up in recent years with the onset of COVID, the top 5 leading causes of death have been the same since 2011. Luckily, there are ways to reduce your risk of falling foul with these chronic conditions.
Though the Australian Bureau of Statistic’s health statistics have been shaken up in recent years with the onset of COVID, the top 5 leading causes of death (Ischaemic heart disease, Dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, Cerebrovascular diseases, Malignant neoplasm of trachea, bronchus and lung, and Chronic lower respiratory diseases) have been the same since 2011 – per Causes of Death, Australia (2020). Every year, the top 5 leading causes of death generally account for a large chunk of all registered deaths – for instance, in 2020 they accounted for more than one-third of all registered deaths. Luckily, there are ways to reduce your risk of falling foul with the top 5 leading causes of death. Read on to learn what causes them, their signs and symptoms, and what you can do to reduce your risk.
Ischaemic heart disease commonly occurs when there is a build-up of plaque in a coronary artery that supplies blood to the heart. This plaque can rupture, cause a clot, and deprive the heart of oxygen, thereby leading to a heart attack.
Ischaemic Heart Disease
What is Ischaemic Heart Disease?
Also known as Coronary heart disease (CHD), Ischaemic heart disease is a chronic disease that affects the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. There is no cure for CHD. On a positive note, there are medicines and treatments available to reduce your risk and improve symptoms.Causes
CHD occurs when the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to the build-up of fatty deposits called “plaque” or “atheroma”. Overtime, these fatty deposits clog the coronary arteries and reduce blood supply to the heart. This process is called atherosclerosis.Signs and Symptoms
- Chest pain (angina)
- Heart attack
- Pain in neck, jaw, shoulder, upper back or abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Feeling cool and clammy
- Light-headedness
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
How to Reduce Your Risk of Ischaemic Heart Disease?
- No smoking: Smoking can damage the walls of your coronary arteries and reduce the amount of oxygen in your blood.
- Healthy diet: Helps to maintain a healthy weight and reduce cholesterol in your blood.
- Reduce stress : Stress increases blood pressure above the healthy level.
- Regular exercise : Keep your heart muscles strong to pump blood effectively to all parts of your body.
- Medications: Lowers blood pressure and cholesterol level, prevents blood clots from forming and treats chest pain.
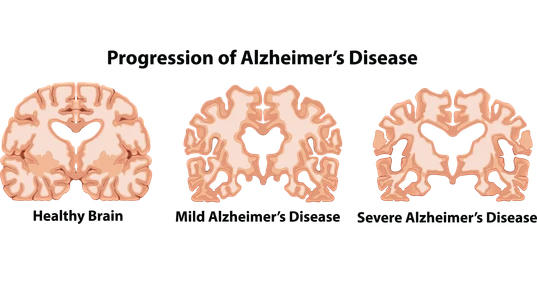
Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's disease causes brain cells to die and for the cortex to shrink, the part of the brain that is responsible for memory and language.
Dementia
What is Dementia?
Dementia is an umbrella term that is used to describe the gradual loss of a person’s memory, intellect, ability to think and socialise with others. Dementia includes other brain disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia and Lewy body dementia.Causes
There are many different types of dementia and the cause of each type varies. Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia, affecting 7 out of 10 Australians with dementia. It is caused by the build-up of certain proteins in the brain, resulting in the death of brain cells and causing the brain to shrink. To learn more about the causes of the different types of dementia, click here.Signs and Symptoms
- Memory loss
- Confusion
- Personality changes
- Behaviour changes
- Apathy and withdrawal
- Loss of ability to perform everyday tasks
- Disorientation to time and place
How to Reduce Your Risk of Dementia?
- Stop smoking.
- Have a healthy diet.
- Stay physically active to increase blood flow to the brain.
- Keep your mind active to build brain cells and strengthen their connections. For instance, find a new hobby, stay socially active, and play mind games such as chess or puzzles.
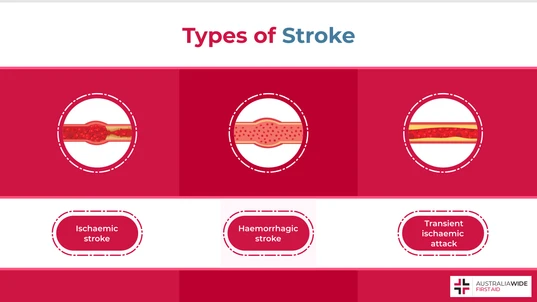
Stroke is the most common type of cerebrovascular disease. A stroke occurs when the blood flow to a part of the brain is disrupted, either by a blood vessel clot or a blood vessel rupture.
Cerebrovascular Diseases
What are Cerebrovascular Diseases?
Cerebrovascular disease is a broad term that is used to describe the conditions that affect the blood vessels in the brain. Cerebrovascular diseases can cause either a lower blood supply to your brain (ischaemia) or bleeding in a part of your brain (haemorrhage). The most common type of cerebrovascular disease is stroke.Causes
- Ischaemic strokes: Embolic stroke occurs when a blood clot travels through the bloodstream and blocks the artery that supplies blood to the brain. Thrombotic stroke, meanwhile, occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the brain are blocked by the buildup of fatty deposits or calcium.
- Haemorrhagic stroke: Intracerebral haemorrhage occurs when the artery in the brain ruptures and bleeds.
Signs and Symptoms
- Balancing problems
- Delirium
- Loss of vision or blurred vision
- One sided muscle weakness
- Slurred speech
- Dizziness or fainting
How to Reduce Your Risk of Cerebrovascular Diseases?
- Maintain your blood pressure in the healthy range.
- Exercise regularly.
- Limit alcohol intake.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Stop smoking.
- Improve your diet: A diet that is high in fibre, fruits, nuts and vegetables and low in saturated fat and salt.
Malignant Neoplasm of Trachea, Bronchus and Lung
What is it?
Malignant neoplasm is a cancerous tumour. It is an abnormal tissue growth that can spread to surrounding tissues and other parts of the body. The cells in the trachea, bronchus and lung grow abnormally. It may grow in the lungs first and spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).Causes
- Genetic changes or mutations in the body cells.
- Family history.
- Smoking damages the cells of the respiratory system.
- Significant exposure to certain heavy metals or substances.
- History of previous lung disease.
Signs and Symptoms
- Persistent cough that lasts for more than 3 weeks
- Shortness of breath
- Chest or shoulder pain
- Fatigue
- Coughing up blood
How to Reduce Your Risk of Malignant Neoplasm of Trachea, Bronchus and Lung?
- No smoking.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Maintain a healthy active lifestyle.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Stay away from substances such as asbestos, radon and other heavy metals.
- Attend all routine cancer screenings to detect any tumour early.
Chronic Lower Respiratory Diseases
What are Chronic Lower Respiratory Diseases?
Chronic lower respiratory diseases affect the airways and other parts of the lungs. According to the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, the two major chronic respiratory diseases in Australia are chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. COPD is an umbrella term that includes emphysema, chronic bronchitis and chronic asthma.Causes
The main cause of COPD is smoking. COPD occurs when the airways in the lungs narrow, obstructing airflow to the lungs and making it difficult to breathe. Exposure to cigarette smoke and other irritants also damage the alveoli or the air sacs in the lungs, making one breathe harder to get enough oxygen. This condition is known as emphysema. Asthma is commonly triggered by allergens, cigarette smoke, irritants such as cleaning products or perfumes and from physical activity.Signs and Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Persistent new cough
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Fatigue
How to Reduce Your Risk of Chronic Lower Respiratory Diseases?
- No smoking.
- Avoid exposure to pollutants, irritants and allergens that can harm your lungs.
- Go for regular check-ups.
- Exercise regularly and eat a healthy diet.
Recommended Resources
To learn more about optimising your health and wellbeing, book a date to learn First Aid with Australia Wide First Aid today!
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/top-5-leading-causes-of-death
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library