Repetitive Strain Injury: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments

Injury
Repetitive strain injuries are a broad variety of injuries that are caused by repetitive motions, which put stress on soft tissues. It is important to know how to identify, prevent, and treat symptoms of RSI, as it debilitates many Australian workers.
Repetitive strain injury is a broad term that consists of many injuries caused by repetitive motions that put stress on the muscles and soft tissues. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a specific injury of the hands and wrists. It is one of the common types of repetitive strain injuries. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, 563,600 Australian had a work-related injury in 2017. The most common cause was “Lifting, pushing, pulling or bending” with 24.2%. 84% of the injured Australians continued to work in the job where their injury occurred. Many workers suffer from injuries to backs, shoulders, elbows, wrists and knees. Today, with millennials joining the workforce and working remotely from their computers, the risk of developing repetitive strain injury is growing. Today, we are going to cover what is repetitive strain injury, the causes of it, its signs and symptoms, the prevention measures to take, home remedies and medical treatments. It is important to understand how this occurs to be able to take actions and protect yourself from injuries at home, work or play.What is a repetitive strain injury?
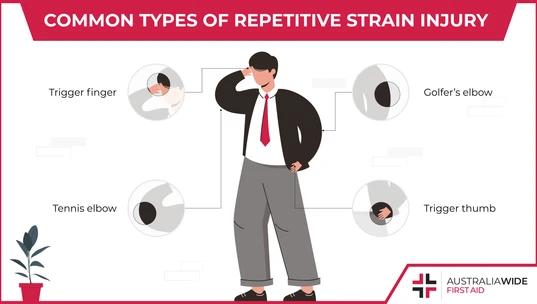
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is also known as occupational overuse syndrome (OOS). Repetitive movements and awkward postures put constant strain on the muscles, tendons, ligaments and nerves. The overworked muscles and tendons cause inflammation and damage to the soft tissues. Repetitive strain injuries is an umbrella term under which many different injuries fall under. One of the most common types of repetitive strain injury is the carpal tunnel syndrome. Other common localised injuries under RSI include, trigger finger, trigger thumb, tennis elbow, tendonitis and bursitis.Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
It is not the same as RSI. Carpal tunnel syndrome is one type of injury that falls under the broad umbrella term ‘Repetitive Strain Injury’. It is caused by stress on the median nerve and the tendons in the carpal tunnel due to repetitive hand movements and awkward postures. For carpal tunnel syndrome, the stress and strain is specifically on the hands and wrists.Where do repetitive strain injuries affect?
Repetitive strain injuries most commonly affect the:- Fingers
- Thumbs
- Hands
- Wrists
- Forearms
- Elbows
- Shoulders and neck
- Knees

Poor body mechanics and postures when lifting or pushing heavy objects is one of the main causes of repetitive strain injuries in the workplace.
Repetitive strain injury causes
RSI occurs when performing repetitive tasks with repetitive motion which puts pressure on the muscles and tendons. Overtime, the constant stress and strain damages the soft tissues. Some causes of repetitive strain injuries include:- Carrying out repetitive movements for a long period of time
- Not enough recovery breaks
- Tensing muscles in the same position for a long time
- Cold working environment
- Poor working environment
- Lifting heavy objects
- Working too fast
- Poor techniques (e.g when swinging a golf club or throwing a baseball)
- Poor postures when sitting, standing or lifting heavy objects
Signs and symptoms
Early signs of RSI:- Soreness, tingling or discomfort when performing a repetitive task.
- Symptoms are relieved when you stop the repetitive motion. The symptoms may be relieved immediately or may take up to a few hours.
- Burning, aching or shooting pain
- Tremors
- Numbness or tingling
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Muscle cramps
- Loss of strength or weakness
- Difficulty performing simple everyday tasks
- Sensitive to the cold and the heat
Repetitive strain injury prevention
It is more challenging to prevent RSI from worsening if the cause of it is work-related activities, for instance, repeated movements of lifting boxes or painting a ceiling. The best way to prevent repetitive strain injury is to avoid overusing or overstressing the muscles and tendons. Some prevention measures include:- Using proper body mechanics when lifting heavy objects.
- Do not try to lift more weight than you can.
- Wearing the correct protective equipment.
- Take regular short breaks from repetitive tasks instead of one long break.
- Stretch frequently. Stretch your body, back, arms, fingers and legs.
- Eat healthy and exercise regularly to keep your body strong.
- When sitting at a desk, avoid slouching and sit straight.
- When typing, avoid bending the wrists. Keep your arms and wrists aligned.

Compression is part of the conservative treatment and it helps to prevent swelling of the injured site.
Repetitive strain injury treatment
A repetitive strain injury is not permanent and will heal over time. Depending on the severity of the injury, the RSI will heal within a few weeks to six months. If you think that you have muscle or tendon strain injury, do seek medical advice and obtain a formal diagnosis from a doctor. Your doctor might also refer you to a physical therapist and an occupational therapist to teach you some repetitive strain injury exercises as well as modify your home and workplace environment to reduce muscle strain and stress.Home remedies
- RICE conservative treatment: Rest (Avoid putting weight on the injured site for 24 to 48 hours. Resting also helps to prevent bruising); Ice (Apply an ice pack for 15 minutes every two to three hours for the first 24 to 48 hours after the injury. It relieves pain and reduces inflammation); Compression (Wrap the injured site with an elastic medical bandage to prevent swelling. Wrap it firmly but not too tight as that will reduce blood flow to the area); Elevation (Keep it elevated above the level of your heart to relieve pain and swelling).
- Warm compress: It should not be used in the first 48 hours after an injury. Heat compress can be applied after the first 48 hours when the swelling has subsided. It helps to increase blood flow to the injured site and promote healing. It also relieves pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs oral form, such as Aspirin and Ibuprofen work to relieve pain and inflammation of the muscles and tendons.
Medical treatments
- Splint: It relieves pressure off the injured site as well as provide extra support.
- Steroid injections: If the pain is severe, a corticosteroid injection is administered to the injury site by a medical professional. It provides short-term pain relief and also reduces inflammation.
- Physical therapy treatment: A physiotherapist will teach you exercises to help strengthen your muscles and improve your body mechanics.
- Surgery: Surgery is rarely needed and is only done when the RSI is very severe. It is also the last resort for when the repetitive strain injury does not respond or improve using the non-invasive approaches, leaving surgery as the only option.
Conclusion and recommended resources
Learn proper body mechanics and keep yourself safe in the work environment. To learn to identify, prevent and manage the symptoms of repetitive strain injury book a date to learn First Aid with Australia Wide First Aid today! If you want to learn more about eating and moving your way to wellness, check out the following articles in our Resource Library:
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/repetitive-strain-injury
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library