First Aid for Scarlet Fever: Prevention, Recognition, and Treatment

How-To
Scarlet fever is a bacterial infection characterised by a red rash on the face, underarms, and groin. Scarlet fever can transmit easily among children. As such, it is important to know how to identify and manage scarlet fever, as it can cause more severe symptoms like vomiting.
Scarlet fever is a bacterial infection caused by group A streptococcus bacterium. Scarlet fever, also known as scarlatina, is a bacterial infection caused by group A streptococcus bacterium. Group A strep bacteria commonly colonize the nose and throat, not always causing illness. But when someone has been infected with group A strep it means that they are exhibiting symptoms and can spread the infection to others. It is the same bacteria responsible for "strep throat" infection. The difference between scarlet fever and strep throat is clearly defined. If a rash develops over the face, underarms, groin, hands, or other parts of the body, then the illness has progressed to scarlet fever. The rash develops because of a toxin secreted by the bacteria.Recognition of Illness
Scarlet fever symptoms typically begin within 2 to 5 days of bacterial transmission. Symptoms most often include:- Sore throat
- Fever
- Rash
- Swollen or white tongue “strawberry tongue”
- Cough
- Swollen lymph nodes and/or tonsils
- Chills
- Headache
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting

'Strawberry tongue' is a common symptom of scarlet fever. It involves a red bumpy tongue and the tongue may also have a white cast.
Prevention of Transmission
Fortunately, scarlet fever does not pose the same mortality risks to our population as it did many years ago. Prompt treatment with antibiotics usually resolves the illness within 2 to 5 days. If strep throat or scarlet fever is suspected, the medical team will first complete a swab to identify what type of bacteria is causing the infection. If the swab test reveals an infection from group A strep, the antibiotics prescribed by your physician will specifically target those bacteria and you should begin to feel a relief of symptoms within 24-72 hours. Prompt use of antibiotics after identification of a group A strep illness typically prevents the development of scarlet fever. Other efforts to prevent the spread of infection include the following:- Hand washing before and after eating or preparing food, after coughing or sneezing, and after using the toilet
- Avoid sharing food and utensils with infected persons
- Avoid close contact with infected persons
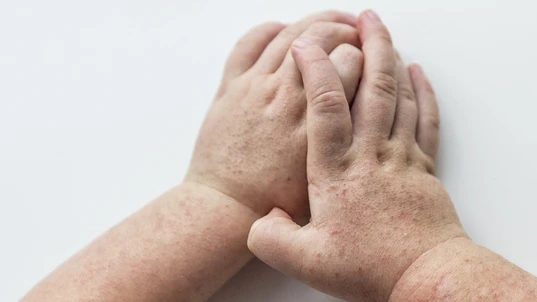
Scarlet fever is most commonly identified by a red, bumpy rash on the face, armpits, groin, and hands.
Treatment and First Aid
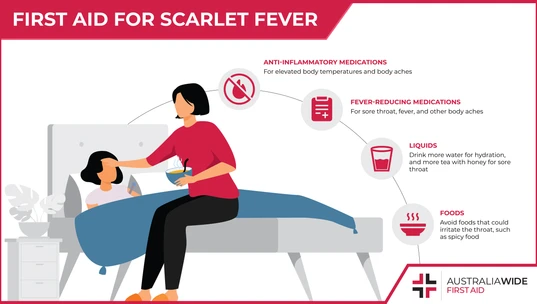
Treatment for scarlet fever includes a round of antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. Antibiotics are effective for shortening the duration of symptoms, reducing the likelihood of transmission to others, and reducing the chances of further complications. When treated with antibiotics you may experience side effects such as nausea and diarrhea. Discuss the possible side effects with your doctor or pharmacist so that you know what to expect. It is important that you take antibiotics as prescribed for the duration of the therapy, even after symptoms have resolved, to ensure that the bacterial infection is appropriately treated. Other first aid therapies that may help reduce symptoms of scarlet fever include:- Fever-reducing medications or antipyretics, such as paracetamol or acetaminophen will help manage elevated body temperatures and body aches. (Consult with your healthcare provider regarding use and dosage)
- Anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen, help treat sore throat, fever, and other body aches. (Consult with your healthcare provider regarding use and dosage)
- Hydrate by increasing fluid intake, primarily water
- Gargle salt water and spit for sore throat
- Drink warm liquids, such as tea, with added honey for sore throat
- Rest often
- Avoid foods that are irritating to the throat such as spicy or rough textured foods
Other Considerations
Children and youth are most at risk for strep throat and scarlet fever because of their closeness of contact which increases the likelihood of transmission of bacteria. Due to the contagious qualities of a bacterial illness, avoid attending large gatherings where you could inadvertently spread the bacteria. Keep children home from school or daycare at least until treatment has been initiated for 48 hours and his/her fever has resolved. For more information on hand washing and how it helps to prevent the spread of infection, check out our hand washing resources in our article library. For more information on first aid, check out the Australia Wide First Aid article library and first aid courses.Resources:
https://www.cdc.gov/groupastrep/diseases-public/scarlet-fever.html https://www.healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/S_T/Scarlet-fever
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/first-aid-for-scarlet-fever
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library