Asthma Action Plan

Allergy and Asthma
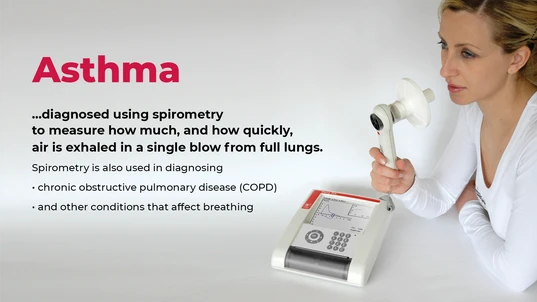
Lung function can be monitored with spirometry or peak expiratory flow (PEF) meter.
Asthma is one of the world's most pervasive chronic diseases. With an estimated 300 million individuals affected around the world, its prevalence is continuously increasing. Australia has one of the highest prevalence rates in the world – more than two million asthmatics. Fortunately, asthma can be effectively treated and, with proper management, good control of the symptoms can be achieved by the vast majority of patients.Asthma control
Asthma control is viewed in terms of symptom control and future risk, meaning a person's asthma is under control when they can:- Enjoy a productive, physically active life. Going to work or school. Being able to exercise and participate in normal physical activities, such as walking to and from the bus stop.
- Have few troublesome symptoms, day or night. No waking at night or losing sleep because of asthma symptoms. The day is not disrupted by breathing problems.
- Avoid most asthma attacks. When asthma is under control, asthma attacks are very rare. Good asthma control means a visit to the emergency department or being hospitalised because asthma is unlikely.
- Use little or no fast-acting reliever or rescue medication.
- Have normal or near normal lung function. Lung function can be monitored with spirometry or peak expiratory flow (PEF) meter.
- Avoid most side-effects from treatment. Many treatments for managing asthma are available and a doctor can recommend which is best for you.
4 simple steps to control your asthma
- Take asthma medication as advised by the doctor. Most people with asthma need two types of medication: a quick-acting reliever or rescue medication to stop asthma symptoms, and a controller medication taken daily to prevent symptoms.
- Know the causes of your asthma symptoms and how to respond to them. Each person with asthma reacts to a different set of risk factors. Take steps to avoid your asthma triggers. Your doctor may tell you to take medication before exercising or working hard if these activities trigger your asthma.
- Work with your doctor. In achieving and maintaining asthma control, your doctor should be your partner. Have checkups 2 or 3 times a year, even if your symptoms have been absent for a while. Ask questions and make sure you continue to understand how to take your medication.
- Act quickly to treat an asthma attack. Know the signs when your asthma is getting worse, how to react, and when to seek emergency medical help. After a severe asthma attack, visit your doctor and review your asthma plan to prevent future attacks.
When your asthma gets worse
Asthma can vary from day to day, over the course of weeks or months. For example, after weeks or months of no symptoms, a change of seasons can agitate your asthma. Recognise the signs when your asthma is agitated or getting worse. This will effectively help to keep your asthma under control. Your asthma could be getting worse if:- Asthma symptoms increase. Wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, or coughing more than twice a week is a sign your asthma is worsening. Waking up a night with troubled breathing is also a sign.
- You need reliever medication more than usual. If you need rescue medication more than twice a week, re-visit your doctor. This is a sign your asthma is getting worse and your doctor may vary your medication to help prevent symptoms.
- You cannot do normal activities. It's a sure sign your asthma is worsening when you are feeling too unwell to participate in physical activities, and going to work, school or exercise is too much for you.
The world's most chronic lung disease
Asthma is:- Characterised by recurrent respiratory symptoms, especially wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
- Heterogeneous – most people with asthma have inflammation in their airways but the symptoms and their intensity differ from person to person.
- Variable – the symptoms wax and wane over time for each individual with asthma. Measurements of lung function also vary over time.
- Allergens (dust mites, pollen, cat and dog allergens)
- Tobacco smoke
- Air pollution
- Exercise
- Strong emotions (crying, stress, laughing hard)
- Chemical irritants
- Certain drugs (aspirin, beta-blockers)
The mystery of asthma
The ongoing increase in asthma prevalence around the world is one the biggest mysteries in modern medicine. Scientists in the 1990s, thought diesel exhaust and pollution could be the cause of the asthma epidemic. They now agree the picture is more complex, differing from individual to individual. For more information, please see our other articles on asthma:
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/asthma-action-plan
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library