Anxiety Disorders: Causes and Symptoms

Mental Health
Anxiety is an umbrella term for a variety of disorders that are characterised by excessive fear or anxiety. It is important to know the symptoms, causes, and treatments of these disorders, as they can impair a person's work, health, and relationships.
Anxiety disorders impact roughly ⅓ of adults, and they differ from typical stress, as they include excessive fear or anxiety. There are many different types of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorders, phobias, panic disorder, agoraphobia, social anxiety disorder, and separation anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorders are treatable, and treatment helps people live normal, productive lives.Generalized Anxiety Disorder
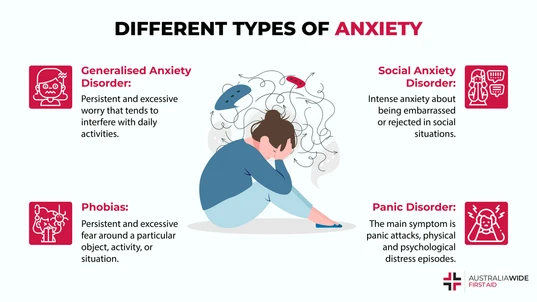
Generalized Anxiety Disorder is characterized by persistent and excessive worry that tends to interfere with daily activities. Symptoms include feeling on edge, having difficulty concentrating, restlessness, trouble sleeping, and muscle tension. In addition, people tend to worry about daily activities, overthink plans and solutions with worst case scenarios, and experience difficulty with uncertainty, indecisiveness, and letting go of worry. Causes of Generalized Anxiety Disorder include differences in brain chemistry and function, genetics, development and personality, and a difference in the way threats are perceived. If one is experiencing Generalized Anxiety Disorder symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to ensure there isn’t a different physical issue causing these symptoms. Some ways to manage these symptoms at home include practising meditation and mindfulness, physical exercise, focus on adequate amounts of sleep, stress management, social support, and avoiding caffeine.Phobias
Phobias are identified by excessive and persistent fear around a particular object, activity, or situation that is out of proportion. Symptoms of phobias include avoiding what it is that causes the anxiety, panic attacks, overwhelming feelings of anxiety, sweating, trembling, difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, tightness in chest, a feeling of dread, and fear of losing control, fainting and dying. Causes of phobias are likely past traumas or incidents, responses that were developed early in life, long-term stress, and genetic factors. If one is experiencing Phobia symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to ensure there isn’t a different physical issue causing these symptoms. Some ways to manage these symptoms at home include practising meditation and mindfulness, physical exercise, focus on adequate amounts of sleep, stress management, social support, and avoiding caffeine.Panic Disorder
Panic disorders often occur around the age of 20-24 and the main symptom of panic disorders are panic attacks. Panic attacks are physical and psychological distress episodes that often include sweating, chest pain, rapid heart rate, trembling or shaking, shortness of breath, and feeling dizzy or faint. Panic attacks can happen very suddenly. Some additional symptoms of Panic Disorder include a sense of impending doom, and fear or loss of control. Causes of Panic Disorder include genetics, intense stress, a temperament that is more sensitive to negative emotion, and changes in function of certain parts of the brain. If one is experiencing Panic Disorder symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to ensure there isn’t a different physical issue causing these symptoms. Some ways to manage these symptoms at home include practising meditation and mindfulness, physical exercise, focus on adequate amounts of sleep, stress management, social support, and avoiding caffeine.Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is an out of proportion fear of being in situations where escape may be difficult. Someone with Agoraphobia may actively avoid a situation, need someone to accompany them for a stressful situation, or endure the high levels of stress and anxiety alone. Some symptoms of agoraphobia include the common fears of public transportation, open spaces, enclosed spaces, being in a crowd, and being alone outside. Symptoms typically last six months or longer, and result in a person avoiding the situation, and having fear or anxiety as a result of exposure to the situation. Some causes of agoraphobia include biology, genetics or health conditions, environmental stress, learning experiences, and temperament. If one is experiencing Agoraphobia symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to ensure there isn’t a different physical issue causing these symptoms. Some ways to manage these symptoms at home include practising meditation and mindfulness, physical exercise, focus on adequate amounts of sleep, stress management, social support, and avoiding caffeine.Social Anxiety Disorder
Social Anxiety Disorder is an intense anxiety around being embarrassed, rejected or humiliated in social situations. People who have Social Anxiety Disorder will often either avoid social interactions, or will endure them with excessive amounts of anxiety. Social Anxiety Disorder typically causes problems with daily functioning. Symptoms of Social Anxiety Disorder include fear of situations that can lead to negative judgment, fear of humiliating oneself, fear of interacting with strangers, fearing others will think that you are anxious, fear of physical symptoms that can result in embarrassment like blushing, fast heartbeat, trembling, and sweating. People who experience Social Anxiety Disorder may also feel that their mind has gone blank in social interaction, and avoid common social situations. Causes of Social Anxiety Disorder include inherited traits and the environment. In addition, if someone has a brain structure with an overactive amygdala (which controls the fear response), they are more likely to experience Social Anxiety Disorder. If one is experiencing Social Anxiety Disorder symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to ensure there isn’t a different physical issue causing these symptoms. Some ways to manage these symptoms at home include practising meditation and mindfulness, physical exercise, focus on adequate amounts of sleep, stress management, social support, and avoiding caffeine.Separation Anxiety Disorder
Separation Anxiety Disorder is classified by extreme fear and anxiety when one is separated from the individual to which they are attached. Symptoms include excessive stress about anticipating being away from loved ones, worry that something bad will happen to loved ones, fear of separation, not wanting to be without a loved one, repeated nightmares, headaches, stomach aches and other symptoms when there is separation. Causes of Separation Anxiety Disorder can be a result of life stress resulting from separation of a loved one or genetics. If one is experiencing Separation Anxiety Disorder symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to ensure there isn’t a different physical issue causing these symptoms. Some ways to manage these symptoms at home include practising meditation and mindfulness, physical exercise, focus on adequate amounts of sleep, stress management, social support, and avoiding caffeine.Conclusion and Recommended Resources
Anxiety disorders are commonplace and are characterised by excessive fear or anxiety. Though there are many different types of anxiety disorders, each of which can impair a person's daily functioning, they are treatable with both formal and at-home support measures. It is important to consult a medical professional or trusted support person if you have any concerns about your mental health. To develop the confidence and know-how to assist someone in a health crisis, book a First Aid course with us today. And if you want to learn more about preventing, identifying, and managing the symptoms of mental health issues, check out the following articles in our Resource Library:
Originally published at
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/resources/anxiety-disorders-causes-symptoms
as part of the Australia Wide First Aid Articles Library









